Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the way we think about transportation, and as their popularity grows, so does the range of options for charging them.
Among these options, AC (alternating current) charging has emerged as a practical and efficient choice for many EV owners.
In this blog, we’ll delve into why AC charging in EV might be the optimal solution for your battery. We’ll also explore its benefits, practical considerations, and how it compares to DC (direct current) charging.
Understanding AC Charging in Electric Vehicles
Before we explore the advantages of AC charging, it’s crucial to grasp how it functions and how it differs from DC charging.
How It Works
AC charging uses an alternating current, which flows in both directions.
This contrasts with direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction.
When you connect your EV to an AC charging station, the electricity needs to be converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger before it can be stored in the battery.
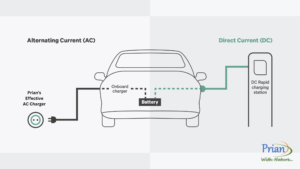
Your EV’s onboard charger handles this conversion.
So, while the charging station provides AC power, the conversion to DC occurs within the vehicle.
Brief on AC vs. DC Charging
AC Charging: This method uses the vehicle’s onboard charger to convert AC power to DC. It’s commonly used in Level 1 and Level 2 home and public chargers.

DC Charging: DC charging delivers direct current straight to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This is the method used in Level 3 charging stations (fast chargers) and is designed for quick top-ups.

Related: AC vs DC Charging in Electric Vehicles
Reasons To Choose AC Over DC For EV Charging
AC charging offers numerous advantages that make it a strong contender for most EV owners. Here’s an in-depth exploration of why AC charging might be the best choice for your electric vehicle:
Cost-Effective EV Charging
- Lower Installation Costs:
Installing an AC charging station is typically more affordable than setting up a DC fast charger.
For example, a Level 2 AC charger installation can range from $500 to $2,000, depending on factors like the complexity of the installation, the electrical capacity of your home, and local labor rates.
This cost is significantly lower than the installation costs for DC fast chargers, which require more sophisticated infrastructure, higher power supplies, and often involve more extensive electrical work.
Additionally, AC chargers are more straightforward to install because they can use existing residential electrical circuits, making them accessible for most homeowners without the need for major upgrades to the electrical system. - Affordable Charging Rates:
AC charging stations, especially public Level 2 chargers, typically offer lower per-kilowatt-hour (kWh) rates compared to their DC counterparts.
The lower cost of AC charging is partly due to the reduced strain on the grid and the fact that AC charging stations have lower operational costs.
Moreover, many utility companies offer time-of-use rates, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles during off-peak hours at even lower costs, further enhancing the economic benefits of AC charging.
Convenience and Accessibility
One of the most significant advantages of AC charging in EV is the convenience of being able to charge your EV at home.
With a Level 2 AC charger installed in your garage or driveway, you can plug in your vehicle overnight and have it fully charged by morning. This overnight charging is particularly beneficial for drivers with consistent daily routines, such as commuting to work or running errands.
The ability to charge at home also eliminates the need to visit public charging stations frequently, saving time and providing peace of mind.
Technically, home AC chargers are usually installed on a dedicated 240-volt circuit, delivering up to 7.2 kW of power, which translates to about 25 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on your vehicle’s efficiency.
Better For Battery Health
AC charging is inherently less stressful on your vehicle’s battery compared to DC fast charging.
When you charge your EV using AC power, the onboard charger gradually converts AC to DC. This is then used to recharge the battery.
This slower, more controlled process generates less heat and reduces the risk of thermal stress. This can degrade battery health over time.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has conducted studies showing that frequent use of DC fast charging, which delivers high power levels directly to the battery, can lead to accelerated battery degradation due to the increased heat and rapid charging cycles.
AC charging in EV, on the other hand, provides a more moderate charging environment. This helps maintaining the battery’s long-term health and capacity.
AC Charging in EV is Simple & Safe
The technology behind AC charging infrastructure is generally less complex than that of DC fast charging systems.
AC chargers typically require only a basic power supply and a simple conversion process within the vehicle’s onboard charger. This simplicity translates into fewer technical issues, lower maintenance costs, and a more reliable user experience.
AC charging operates at lower power levels than DC fast charging, which contributes to a safer charging environment. The lower voltage and current reduce the risk of overheating, electrical faults, and other potential hazards.
According to a safety report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), AC chargers have a lower incidence of safety issues compared to high-power DC chargers. The controlled power delivery in AC charging minimizes the chances of thermal runaway or other dangerous conditions that can occur at higher power levels.
Overall, AC charging in EV offers a balanced approach to powering your EV, combining cost-effectiveness, convenience, battery health preservation, and safety.
Whether you’re charging at home or at one of the many available public stations, AC charging provides a reliable and user-friendly option for keeping your electric vehicle ready to go.
Wrapping Up
Choosing the right charging method is crucial for ensuring a seamless and efficient driving experience.
AC charging stands out not just for its practicality and cost-effectiveness, but also for the way it aligns with the long-term goals of EV ownership.
Whether you’re looking to maintain the health of your battery, take advantage of convenient home charging, or simply make a smart investment in your vehicle’s future, AC charging offers a reliable and thoughtful solution.
As you continue on your journey with your EV, embracing the benefits of AC charging can help you get the most out of every mile.


Leave a Reply